
 |
Newton studied in Cambridge and was later offer the Physic chair there. He made most of his greatest discoveries in the two years, 1666 and 1667, because he had to stay in his home during this period due to the plague. He is famous for his discovery of gravitation, as anybody knows about the story of "Newton's apple". The authenticity of this story is highly doubtful. He laid the foundation of classical mechanics by describing the 3 laws of mechanics, that all physics students are familiar with. He is also the discoverer of Calculus (which he called the "Theory of Fluxions and Inverse Fluxions"). He generalized the Binomial Theorem to negative integer and fractional powers. He also worked extensively on Optics and he contributed much to analysis of infinite series. He was always reluctant to publish his results until he can affirmatively prove that they are true. This led to a bitter dispute with Leibniz as to who is the 'true' founder of calculus. His most famous book Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy), in short Principia, was published only after much persuasion from his close friend, Sir Edmund Halley (of Halley's comet fame). |
This is call the indefinite integral of f(x).
Newton-Raphson's Method of Approximation
This is an iterative
method of obtaining the roots to an equation. It is written as
where f'(x) is the first derivative of f(x).
E.g. it is impossible to obtain the roots of 5cos(x) = ex analytically. However, we can solve for it numerically via Newton-Raphson's Method, by setting f(x) = 5cos(x) - ex
Netwon's First Law: Every object stays at rest or move with constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force. This is the concept of inertia.
Netwon's Second Law: The force acting on an object is proportional to the mass of the object and the rate of change of momentum of the object. This results in the famous equation:
where F is the force, m is the mass and a the acceleration of the object. It also provides the definition of 1 Newton of force.
Netwon's Third Law: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
With these 3 laws and a few definitions, many phenomena in mechanics can be discovered. For example, together with the definition of 'Work', you can show that the Kinetic Energy of an object with mass m and speed v is 1/2 mv2.
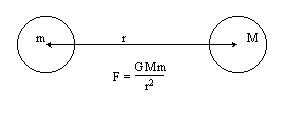
Newton showed that the gravitational force between two objects is proportional to the product of the masses (M and m) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between them.
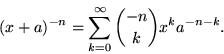
We now know that this is in fact true for all real powers.
Return to Maths Homepage